In recent years, we’ve seen more robots in smart cities, factories, and homes. However, most of these robots are controlled by traditional algorithms, meaning they have specific tasks and don’t learn much from their environment. On the other hand, there’s a type of artificial intelligence called embodied AI. These AI agents, like robots or virtual assistants, can interact with and learn from the world around them. They have sensors, like cameras and pressure sensors, to collect data from their environment. Then, they use AI systems to analyze this data and learn from it.
Embodied AI can be a big help in various areas like manufacturing, entertainment, medical care, and warehouses. For example, it can make manufacturing faster, make games more fun, and help with tasks like surgery and helping older people. It’s especially important now because there aren’t enough workers, especially in rich countries. In recent years, there have been a lot more robots used in manufacturing. For example, in the U.S., there are now 255 robots for every 10,000 workers, which is a 45% increase since 2015. You may also like Meta Llama 3: Most Powerful Publicly Accessible LLM Currently Available.
Table of Contents

What’s Required For Embodied AI To Spread
At Qualcomm AI Research, we’re exploring how generative modeling can improve embodied AI and robotics. Our goal is to move beyond traditional robotics by enabling new capabilities like:
- Understanding scenes with diverse vocabularies.
- Interacting naturally through spoken language.
- Using large language models for reasoning and common sense.
- Performing dynamic actions and closed-loop control using language models or diffusion models.
- Integrating vision, language, and action in models.
For robotics to advance, we need data efficiency, fast response times, strong privacy protection, and efficient sensor processing. To meet these needs, Qualcomm Technologies is developing platforms like the Qualcomm Robotics Platforms. These platforms, powered by the Qualcomm AI Engine, enable the creation of smarter, more independent, and more advanced robots, opening up new possibilities for innovation. Read also Codeium AI Review, Features, Price, Use Cases 2024
An Architecture For Robot Motion Planning That Uses Data Dfficiently
While AI processing at the edge is a good foundation for creating embodied AI applications, there’s a major challenge to address. Unlike internet AI, which learns from fixed datasets like ImageNet, embodied AI learns by interacting with the physical world. This type of data isn’t easily available online and can be costly to obtain. To tackle this issue, the Qualcomm AI Research team has developed a new model called “Geometric Algebra Transformers” (GATr), which enhances robots’ understanding of their surroundings. Read also The Latest NVIDIA Blackwell AI Superchip and Architecture
GATr focuses on the geometric aspects of the environment using geometric algebra representations and equivariance. It’s designed to be scalable and versatile like transformers, delivering impressive results even with limited data. The architecture comprises three main components: geometric algebra representations, equivariant layers, and a transformer architecture. Read this interesting article The Future of AI is Faster: Meta’s Next-Gen MTIA Chip Speeds Up Learning
Geometric algebra representations: GATr employs geometric algebra, a mathematical framework, to represent and process geometric data efficiently. This allows it to handle various types of geometric data without needing changes to the network structure.
Equivariant layers: Equivariant neural networks ensure that the model can recognize objects regardless of their orientation or movement. This improves the efficiency of AI-powered robots by reducing the amount of data needed for training.
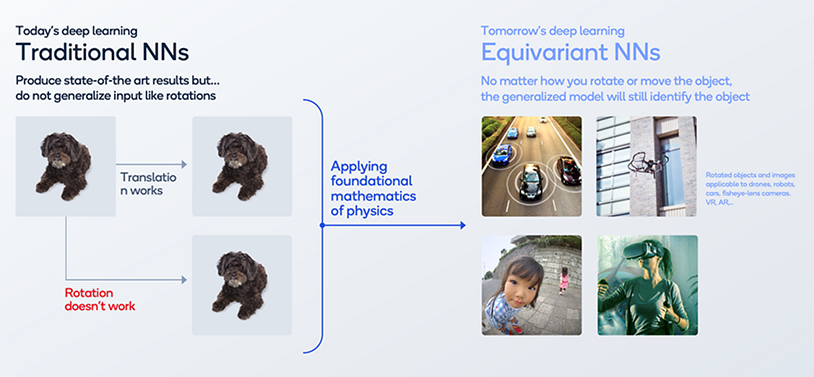
Transformer Architecture
GATr builds upon the transformer architecture, which is known for its effectiveness in generative AI. In transformers, a key process called self-attention is used. We’ve introduced an equivariant alternative to self-attention in GATr. This maintains the scalability advantages of traditional self-attention while offering improved performance.
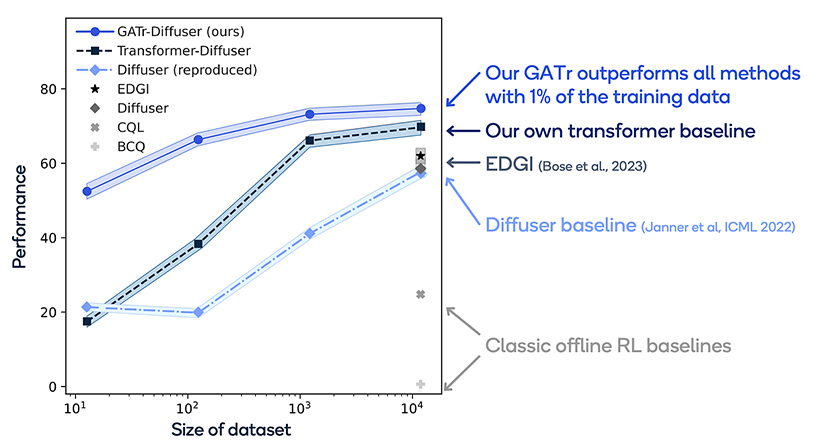
GATr Performs Better Than Other Advanced Architectures Currently Available
Think of our approach to generating a robot’s path plan similar to how you’d clean up a blurry image using a diffusion model. Instead of refining an image, we refine the trajectory of a robot. And instead of using the usual U-Nets for this, we employ GATr, which is more effective.
We put our method to the test on various tasks, like stacking blocks with a robot. As shown in the graph, even with just 1% of the training data, our approach outshines previous methods. And as we increase the number of items, our method remains superior. Plus, GATr can handle large amounts of data, surpassing other techniques in geometric deep learning.
Working To Bring Embodied AI Into Reality
We think that embodied AI can make a big difference in fields like manufacturing and healthcare. Our team at Qualcomm AI Research is developing various projects in embodied AI. For example, we have a model for helping robots plan their movements in a smarter and more efficient way. You might also want to look into our work on “Uncertainty-driven Affordance Discovery for Efficient Robotics Manipulation,” which helps AI-powered robots make better decisions.
We believe that on-device generative AI will continue to be important for embodied AI. Additionally, we’re exploring how equivariance can help AI better understand 3D images and videos. Keep an eye out for more research in this area.
